Protect your Future
Safe Book
Protect yourself
Your Health
Preventing sexually transmitted diseases safeguards your health and helps you and your loved ones stay healthy.
Your Freedom
Your freedom and freedom to choose, to achieve your dreams and live a full sexually active life cannot exist without correct information on how to behave during sexual intercourse and complete knowledge of all the risks you run when you don’t consider disease prevention. Your objectives are your full sexual freedom and respecting those who share this with you.
Knowing your sexuality
You can’t rely on your friends teaching you about your sexuality, from their experiences or indeed from the internet, which flashes up images that you have not even requested. Learn to recognize new signals your body is sending you, decipher them and enrich your sensibility. Observe the changes you are going through, know what is the results of your experiences and what your prejudices and fantasies are before developing your sexuality. Live your freedom with joy.
Information on your sex life
Do you have questions or doubts? Are you simply curious? Do you need to ask advice about your sex life? Ask someone who can give you a professional reply. Don’t be left with incomplete or incorrect information leaving you feeling anxious.
Do you know that where you live there are family advisors, look for them on the internet and don’t be afraid to contact them. You will find experts who listen and understand you as if you were an adult and can advise you whether you need to talk with a doctor, gynecologist, andrologist, sexologist or a psychologist.
Don’t be content with do-it-yourself answers, you wouldn’t do so regarding other aspects of your life so why would you do it regarding your sex life?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Sexually transmitted diseases are diseases which are transmitted from one person to another during sexual intercourse. The most notable are; Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Viral Hepatitis, Human Papillomavirus (HPV), Syphilis, Trichomoniasis and HIV Infection (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
Valid indications to reduce the risk of contracting STDs
Abstinence
The safest, and indeed the least pleasurable way is not having sexual intercourse.
Vaccinations
Vaccination against Hepatitis B is absolutely necessary and is obligatory in Italy since 1990.
Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B and the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) are preventable in a safe and efficient way by means of vaccination.
Monogamy
If you are sure to have sexual intercourse with one person only and that person will be strictly faithful to you, you have an excellent solution to reduce the risk of contamination of STDs. You both should check for any infections at the moment you decide to choose a monogamous relationship (closed relationship) and go for tests to be absolutely sure.
This choice should always be discussed with your partner and will require absolute trust and honesty from the couple.
Reducing the number of sexual partners
Reducing the number of people with whom you have sexual intercourse will reduce the risk of contracting STDs. It’s very important that you and the people you have sexual intercourse with, go for regular check-ups and testing and take care of your health. It’s necessary to inform your partners of your state of health and you can ask them about theirs even although any reassurances cannot eliminate all risks.
Using a Condom
The correct and habitual use of a condom is the best way to avoid STDs. Always use a condom when having vaginal, oral or anal intercourse.
Using Vaginal and Anal Lubricants
Using lubricants, particularly with anal penetration, prevents the condom breaking and therefore reducing the risk of small tissue lesions, reduces the risk of infections including HIV.
The lubricants must be suitable products and not cause damage to the condom (such as oily lubricants like hand creams, Vaseline, Crisco etc.) and do not irritate the mucous membranes of the body parts in contact during penetration.
Diagnostic Testing
Being aware of having a STD is the best way to break the chain of infection. Ask your doctor or consultant to carry out the recommended testing for STDs. Once the testing is completed other aspects of your sex life which are not clear from testing alone can be discussed. Talk to your doctor plainly and without embarrassment about any sexual intercourse you have had and ask your partner to do the same.
You must inform your partner of the state of your health. If you find out you have an infection you have to cure yourself and make sure your partner cures him/herself. Only in this way can you interrupt the chain of future reciprocal infections.
Always ask your doctor, consultant or a clinic against infectious and venereal diseases (STD clinic) for information
Chlamydia, Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma
What are Chlamydia, Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma infections?
Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis) , Mycoplasma (Mycoplasma genitalium) and Ureaplasma (Ureaplasma urealyticum) infections are sexually transmitted diseases which can affect both men and women. They are all very similar and avoiding any cure may result in serious and permanent damage a woman’s reproductive system making it difficult or impossible to have children. The most common and perhaps the most dangerous is the chlamydia infection.
How is the Chlamydia infection spread?
Anyone who has the chlamydia infection can infect their partner through vaginal, anal or oral sex. If the infected partner is male he can transmit the infection even without ejaculating. Even though the infection has been cured in the past, sexual intercourse with an infected partner can result in a renewed infection.
What are the risks of Chlamydia?
Every unprotected intercourse (vaginal, anal or oral) can transmit chlamydia. Young people, with an active sex life both heterosexual and homosexual are most at risk of infection because of both behavioral and biological factors. Young women under 25 must ask their doctor to check for chlamydia symptoms. If the test result is positive then the partner must be informed and both parties must be treated at the same time thus avoiding mutual reinfection
Chlamydia infection symptoms
Very often chlamydia does not present any symptoms at all but damage to a woman’s reproductive system can be very acute all the same.
The most common symptoms are; abnormal genital discharge in both men and women and a burning sensation when urinating. If the infection is rectal then the discharge is from the anus, can be painful and bleeding can occur
How can I protect myself from Chlamydia?
Reducing the risk of contamination of the chlamydia infection is obtained by:
● a long term, strictly monogamous relationship for both partners
● a simple test to check both partners result negative to the infection
● correct use of a condom each time sexual intercourse occurs.
Gonorrhea
What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea (colloquially known as the Clap) is an STD which can affect both men and women and is very common from age 15 to 24 years old. It can affect the genitals, the rectum and the throat. If not cured it can cause serious damage to your health. The treatment prescribed by a doctor must be followed carefully because there are many reported cases of the gonorrhea infection which is resistant to antibiotics.
How is Gonorrhea spread?
Anyone infected with gonorrhea can infect their partner through vaginal, anal or oral contact. If the infected partner is a man then it can be transmitted whether ejaculation occurs or not.
Even though the infection has been cured in the past, sexual intercourse with an infected partner can result in a renewed infection.
What are the risks of Gonorrhea?
Every unprotected intercourse (vaginal, anal or oral) can transmit gonorrhea. You must speak honestly and candidly to your doctor who will indicate which test to carry out to find out if you are infected with the gonorrhea bacteria. Given that gonorrhea can be transmitted anally and orally, young homosexuals must get checked out on a regular basis. If the diagnosis is positive the partner must be informed and treated at the same time thus avoiding mutual reinfection.
Gonorrhea Symptoms
Very often gonorrhea does not present any symptoms at especially in women but the results of not treating the infection can be very acute indeed.
The most common symptoms are; abnormal genital discharge in both men and women and a burning sensation when urinating and in women, bleeding can occur during the middle part of the menstrual cycle. The discharge can be mucous or pus from the vagina and the urethra (last section of the urinary tubes). If the infection is rectal the discharge is from the anus and can be painful and bleeding can occur. Anal itchiness and painful bowel movements can occur.
How can I protect myself from Gonorrhea?
Reducing the risk of contamination of gonorrhea is obtained by:
● a long term, strictly monogamous relationship for both partners
● a simple test to check both partners result negative to the infection
● correct use of a condom each time sexual intercourse occurs.
Viral Hepatitis
What are Viral Hepatitis?
A viral hepatitis is a viral infection which strikes the liver and is caused by various viruses. The most common type are Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C. They present similar symptoms but are spread in different ways and have differing levels of seriousness.
Hepatitis A
What is Hepatitis A?
Hepatitis A is an acute disease which can last from a few weeks to several months. Usually the patient makes a full recovery. It is the most common type of hepatitis in Italy where the illness is endemic (that is to say frequently occurs) especially in the Southern regions. It is present worldwide especially in Central America, South America, Africa, Middle East, Asia and Western Pacific.
How is Hepatitis A spread?
Hepatitis A is spread by ingesting material of fecal origin, contaminated food or drink or traces of fecal material during sexual intercourse. Normally hand washing after using the bathroom is good practice to prevent the transmission of the infection from one person to another. Oral sex around the anal region with an infected partner carries a very high risk of infection.
Preventing Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A can be prevented by vaccination. The vaccination is recommended in all children, travelers (who can be at risk of poor hygiene practices) and people whose have a risky sexual practices. Ask your doctor for the test to know if you already are protected against hepatitis A by your immune system having produced antibodies from a previous infected from which you were cured or from a childhood vaccination which you will not remember. If you are not protected then ask for the two doses of vaccine to avoid exposure. Keep up the good practice of carefully washing your hands with soap and water in the meantime.
Hepatitis A symptoms
There can be no symptoms at all with hepatitis A. The blood test can show up any infection immediately and the infected person’s state of health. Symptoms can include fever, nausea, vomit, loss of appetite, fatigue, very dark urine, grey stools, stomach cramps, jaundice (yellowish colour of the skins and whites of the eyes).
Hepatitis B
What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a disease of the liver caused by the HBV virus (Human Hepatitis B Virus).
The personal history of infection by HBV varies according to the age at which the infection was caught. More than 90% of the people infected with HBV are able to eliminate the virus in 6 months. In this case the HBV virus causes an acute infection which however does not become chronic. The other 10% of infected people are not able to destroy the virus completely and can expect to suffer from a chronic and long lasting illness. Regarding infections caught by infants the proportions are reversed with 90% becoming chronic and 10% able to overcome the infection. The chronic evolution of such a disease can result in a series of complications for the patient such as fibrosis, cirrhosis or liver disease, liver failure and tumor of the liver.
How is Hepatitis B spread?
Hepatitis B is a disease of the liver caused by the HBV virus (Human Hepatitis B Virus). The virus is spread through bodily fluids such as blood, seminal liquid and vaginal secretions. The most commons ways to become infected are:
● unprotected sex
● sharing razors and toothbrushes
● sharing syringes which should be used only once.
Hepatitis B can also be spread from mother to child during childbirth.
The most common way of transmission is by sexual activity and the hepatitis B virus is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV (the virus which causes A.I.D.S.)
Hepatitis B prevention
Hepatitis B can be prevented by vaccination. The vaccination is recommended to all those who are sexually active and especially those who have many different sexual partners, people who have STDs and people who have infected partners. Ask your doctor to prescribe the 3 usual doses of the vaccination.
Hepatitis B symptoms
Hepatitis B can show no symptoms at all. Most people with hepatitis B, both in the acute and chronic form, are asymptomatic (show no symptoms). If it is a case of hepatitis B symptomatic there can be a series of unspecific symptoms such as weakness, fever, loss of appetite, muscular pain, abdominal pain. A typical sign of hepatitis B is jaundice (yellowish colour of the skins and whites of the eyes). A blood test can clarify immediately whether or not a person is infected or not.
Hepatitis C
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a disease of the liver caused by the virus HCV (Human Hepatitis C Virus). It is spread by direct contact with the blood of an infected person. Hepatitis C can either show no symptoms at all or manifest itself as an short acute illness lasting 6 months from infection. It can range from a slight illness to a complete hospital recovery. In 75-8% of cases, the illness can become chronic and cause serious damage to the liver, liver disease and even tumor of the liver.
How is Hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C can spread when the blood of an infected person comes into contact with the blood of a healthy person. This can happen for example when infected syringes used for taking drugs are shared. It is most frequently transmitted sexually by people with many partner, those who already have STDs or HIV (given that rectal mucous is more fragile and the weaker immune system) and the biggest risk group is men who have homosexual intercourse and that are HIV positive.
Hepatitis C prevention
Hepatitis C can be prevented by avoiding:
● sharing syringes for injecting drugs, steroids or other substances;
● using personal objects of other people like razors, nail scissors, toothbrushes which can have traces of infected blood ;
● have tattoos or piercings done in unauthorized places which don’t use sterile instruments.
The following people should be tested for hepatitis C with a frequency recommended by the doctor:
● those who habitually inject themselves with drugs and other substances or those who have done so in the past;
● those who have abnormal liver test results or who have liver disease;
● those who are on dialysis, that is to say those who have serious problems with kidneys and have to have kidney filter therapy
Hepatitis C symptoms
Hepatitis C doesn’t necessarily show any symptoms. A blood test can immediately establish if a person is infected or not. Most people with acute or chronic hepatitis C are asymptomatic. For this reason hepatitis C can remain undiscovered and undiagnosed for many years before showing any clinically relevant signs. The symptoms do not differ significantly from the other hepatitides and include weakness, joint pain, itchy skin, muscular pain, stomach ache and jaundice (yellowish colour of the skins and whites of the eyes).
Hepatitis C is diagnosed by means of a blood test. Routine blood tests do not specifically include testing for HCV so it must be explicitly requested to by the doctor to carry out the test for Hepatitis C. For this reason the majority of asymptomatic hepatitis C sufferers are unaware they have the disease. It may be discovered during blood donation where all blood is routinely screened.
Genital Herpes
What is Genital Herpes?
Genital Herpes is an common STD caused by a virus called Herpes Simplex. A common form of the herpes virus appears on the lips (labial herpes). One person in six, from the age of 14 to 49 years has come into contact with this virus. Even though there are no obvious lesions an infected person can transmit the infection to a partner.
How does Genital Herpes spread?
Genital Herpes is spread by vaginal, anal or oral sex.
It can be recognized by the contagious lesions and blisters filled with liquid which contain the virus. The infection can be transmitted simply by skin contact.
Genital Herpes prevention
Being active sexually and having partners who are potential carriers of the herpes virus the best way to reduce the risk of infection is to use a condom in the correct way every time there is sexual contact. This is good protection but not absolute since the transmission can take place on parts of the body not protected by the condom.
Genital Herpes symptoms
Many people who have the herpes virus show no symptoms or very slight symptoms which can be confused with other skins irritations. Generally the first sign of genital herpes is painful lesions on and around the genitals, rectum and mouth which look like small blisters full of liquid. When the blisters burst, the resulting sore can take a while to heal. There can also be similar symptoms to the flu (fever, joint pain, headache and swelling of the lymph nodes. (sometimes wrongly called lymphatic glands). There is no complete cure. You need to see a doctor who will correctly diagnose the virus and prescribe a therapy which will make the lesions due to Genital Herpes disappear.
HIV infection (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
What is HIV infection?
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus which is found in bodily fluids (particularly blood, sperm and saliva) and attacks certain cells of the immune system called CD4 cells or T cells. When the virus destroys many of these cells the immune system is no longer able to protect against infection and disease. A very serious diseases called AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). Currently there is no cure for HIV but there are drug therapies (antiretroviral therapy ART) which prevents the deterioration of the immune system and reduces the capability of infected persons transmitting the virus to others.
Antiretroviral therapies must be taken for the rest of the patient’s life. HIV infection is a serious disease.
HIV Prevention in anal and vaginal intercourse
There are some basis rules to prevent HIV infection:
● Choose low risk sexual activities. Sexual activities without exchanging bodily fluids (blood, sperm) like reciprocal masturbation, do not carry risks of transmitting the HIV virus. Kissing does not transmit HIV. Unprotected anal sex is riskier than vaginal intercourse because of the tissues in the rectum and intestines are more fragile. Passive anal sex is the riskiest of all types of penetrative sexual intercourse.
● Always use a condom in the correct way. Using a condom is the best way to protect yourself from HIV.
● Reducing the number of sexual partners. Increasing the number of partners increases the risk of meeting a partner who has HIV or has other STDs.
● Go to a STD clinic immediately after sex with a high risk of HIV infection. If you have had unprotected anal or vaginal sex or if the condom broke, with a partner with HIV or potentially with HIV, the STD clinic or the Infectious Disease Unit can administer a preventive medicine post HIV exposure (PEP). It must be clear that this is an exceptional measure and the prevention of HIV must remain with the correct and continuous use of a condom.
● Take the HIV test (HIV positive test) at least once a year and encourage your partners to do the same
● Treat other STDs because they increase the risk of contracting HIV and encourage your partners to do the same
● If your partner/partners is/are HIV positive encourage them to follow the anti-HIV therapy. These therapies reduce the quantity of the virus in the blood and sperm to such an extent that they are virtually undetectable in laboratory examinations. These drug therapies enable the HIV positive person to live a long and full life and reduce the possibility of transmitting the HIV virus to others.
HIV Prevention in Oral Sex
Don’t let your partner ejaculate in your mouth without protection. It is good practice to always use a condom. The riskiest of all oral practices is that of the mouth and penis with ejaculation in the mouth. The risk is less (although still present) in practices between mouth and vagina o anus. The presence of sores or lesions or other STDs on these organs increases the risk of HIV transmission. If your partner is HIV positive and follows the drug therapy correctly the risk of infection is low.
Use of Lubricants
Using lubricants, particularly with anal sex, prevents the condom breaking this reducing the risk of infections (including HIV).
The lubricants must be suitable products and not cause damage to the condom (such as oily lubricants like hand creams, Vaseline, Crisco etc.) and do not irritate the mucous membranes of the body parts in contact during penetration.
HIV Prevention with drug use.
Always use a condom and take an anti-HIV test at least once a year.
If you must inject drugs or steroids, hormones, silicone fillers or other fillers used in cosmetic surgery without medical supervision then remember NEVER share your syringe, the sterilised water you inject or the vessels you use to dissolve the powders to inject. When you inject yourself avoid contact with blood of others who share your injecting habits.
Genital Infection from Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
What is HPV?
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common STD, so much so that practically everyone with an active sex life has been in contact with the HPV virus. There are many different types of HPV which can cause many diseases from annoying genital warts and others much more serious like cancer.
How is HPV spread?
Vaginal, anal and oral sex with an infected person with HPV, even though showing no symptoms, can transmit the disease. Symptoms can develop a long time after infection and this can make it difficult to know the origin of the infection.
HPV prevention
There are several ways to reduce the likelihood of being infected by HPV
● Vaccination – there are several vaccines against HPV available in Italy. 11/12 year olds can already be vaccinated and in any case both men and women are recommended to have the vaccination before they reach the age of 26.
● Cervical Cancer Screening – all women from 21 to 65 years old can prevent cervical cancer by having a routine HPV screening.
● Correct use of condoms – if you have sexual relations with someone who is not completely faithful then using condoms can reduce the risk of HPV infection but not completely eliminating the risk since some infected areas can be out with the area protected by the condom.
HPV symptoms
Many people never develop any symptoms whereas others – men and women – discover the appearance of warts or lesions on their genitals or the anal region or some women can discover to have abnormal cells on the cervix. Pre-cancerous or cancerous lesions can be identified during a PAP test, a simple and painless examination can offer an early diagnosis when the disease can be easily treated. Those who have unprotected anal sex can develop cancer of the anal mucous membrane.
Syphilis
What is Syphilis?
Syphilis is a STD which can have very serious consequences if not treated correctly. Those who have sexual relations with several partners are urged to take a syphilis test periodically.
How is Syphilis spread?
Syphilis can be spread through direct contact with an infected sore or lesion which the infected person can have on their penis, vagina, anus, rectum, lips or in the mouth. Attention: Syphilis can be caught again through sexual contact with an infected person even after it has been treated and cured.
Syphilis prevention
Reducing the risk of contracting syphilis can be achieved by:
● Having a monogamous sexual relationship (closed relationship) by both partners
● Both partners being tested and resulting negative to the syphilis
● Correct use of condom for each sexual contact. The condom prevents direct contact with the syphilis sores. These sores can be present in areas not covered by the condom so although protection is high, it is not absolute.
Syphilis symptoms
If syphilis is not cured there are various stages of the disease:
● Primary Syphilis: a lesion appears (rarely more than one) in the spot where infection occurred. The lesion looks like a small sore. Because it is not painful and it can be in a place hidden from view, it can pass unnoticed. The lesion heals in 3-6 weeks even if not treated. If not treated it can develop into
● Secondary Syphilis; this presents itself as a skin rash, sores in the mouth, in the vagina and around the anal zone. These symptoms disappear with or without treatment. Without treatment however the disease continues into
● Latent and Tertiary Syphilis. When the symptoms of Secondary Syphilis disappear, the disease enters a latent state. This latent state can remain like this with no more symptoms but the disease can continue to damage internal organs. Damage to the organism during this phase is no longer curable. After a very long period of time (15-30 years) the disease can enter the Tertiary Stage which can damage the central nervous system, cause difficulty in muscular movement and coordination even causing paralysis, absence of sensitivity (to hot or cold and painful stimuli) and dementia.
Trichomoniasis
What is Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is very common especially in women but more often than not the infected persons do not know they have the parasite which causes the infection.
How is Trichomoniasis spread?
The parasite (Trichomonas Vaginalis) prefers to invade the vulva and vagina in women and in the urethra in the male. The infection is passed from the infected sex organs of the woman to the urethra of the man or vice-versa. It can also be transmitted during female homosexual intercourse, from vagina to vagina using for example sex toys. After curing the disease it is easy to be infected again.
Trichomoniasis prevention
Using a condom every time you have vaginal intercourse reduces the risk of infection. It is good practice to talk to your partner and let them know if you have had recurring episodes of irregular discharges, burning sensation during urination, genital sores. If this is the case it is better to seek medical advice for a diagnosis since the symptoms can appear and disappear in an irregular way.
Trichomoniasis symptoms
70% of the people infected by Trichomoniasis do not present any symptoms but can transmit the parasite. Women can experience itchiness, burning sensation, rashes and genital sores. Urinating can be uncomfortable. There can be whitish or greenish discharge with an unpleasant smell from the genitals. Sexual intercourse can be painful and uncomfortable. Men can experience itching or irritation inside the penis with discharge. There can be a burning sensation after ejaculation or urinating. Without a correct treatment the infection can continue for months or years. Re-infecting a partner is very easy indeed. Fortunately there is a cure.
Parasites of the Human Body
Lice and Pubic Lice (Crabs)
What do lice and pubic lice look like?
Pubic lice (crabs) are parasites which inhabit the pubic area and hairy parts of the body except in the hair.
They are present in three forms;
● Eggs (or nits), these can be difficult to see and are attached to the hairs and look like whitish spots. After 6-10 days the hatch and become
● Nymphs; immature lice which feed on blood and become adults in 2 to 3 weeks
● Adult lice; these are visible to the naked eye. They look like small crabs (see photo below). They survive on blood and they can survive up to 2 days without being in contact with the human body.
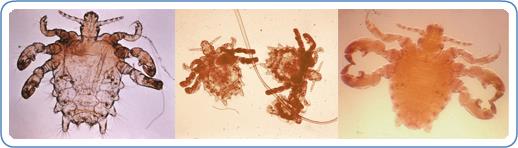
Fonte: Center for Diseases Control and Prevention – Ectoparasitic Infections
How are Pubic Lice spread?
Pubic lice are spread through sexual intercourse. The adult lice cannot survive far from the human body and are able to move with ease over the skin to different areas of the body.
Pubic Lice ( Crabs) Infestation Symptoms
The presence of Pubic Lice causes itching of the pubic area and the infested hairy areas of the body.
Eliminating Pubic Lice (Crabs)
Ask your doctor to confirm if you have Pubic Lice and ask them to prescribe a lotion or cream to apply to the infested area. Follow carefully the instructions on the product used. Inform any partners you have had in the preceding couple of weeks so they can also follow the same treatment.
Scabies
What does Scabies look like?
The scabies mite is microscopic. It looks like the image below but it is not visible to the naked eye. It burrows little tunnels in the uppermost layer of the skin where it lives and reproduces.
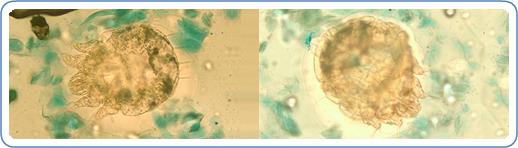
Fonte: Center for Diseases Control and Prevention – Ectoparasitic Infections
How is Scabies spread?
Scabies is spread by means of prolonged contact of the skin with an infected person. This happens in particular during sexual intercourse. It can also be spread in places where many people live in close proximity.
Scabies’ Symptoms
Scabies causes intense itching and irritation of the skin especially during sleep. The itchiness can be all over the body or in localized areas such as wrists, elbows, between fingers and toes, nipples, penis. The first signs of infestation occurs 4-6 weeks after contamination. If however it is a re-infestation then itching occurs after 4 days.
Eliminating Scabies
You must consult your doctor who will prescribe a localized insecticide treatment. There is also an oral treatment. Avoid a self-diagnosis and medication since you must be certain it is Scabies and the specific treatment for Scabies must be followed very carefully. Any clothing and bedclothes which have been in contact with the Scabies mites must be washed in hot water. Since the Scabies mites cannot survive more than 72 hours away from the human body then it is sufficient to avoid anything or anyone potentially infected for this period.
Inform your partners with whom you have had sexual activity within the last couple of weeks so they can go for a medical check-up to see if they have been infected or not.
Other diseases transmitted by sexual contact
Bacterial Vaginosis
What is Bacterial Vaginosis?
Bacterial Vaginosis is a the most common vaginal infection in women from 15-44 years old. It is an infection caused by bacteria which upsets the normal microbial equilibrium in the vagina. It is not considered an STD.
It must not be confused with genital fungal infections usually caused by Candida Albicans which is very common in women but are not acquirable through sexual activity. On the contrary, fungal infections which are normally present on the patient’s skin or in the gut microbiota can multiply excessively due to a large number of factors. The high incidence of vaginal candidiasis can be caused by the increasing use of wide spectrum antibiotics, women taking contraceptive pills, menstrual flow, diabetes mellitus, too tight underwear, the suppression of the cell-mediated immunity following use of medicines or from HIV infection.
How is Bacterial Vaginosis spread?
It is not really known how Bacterial Vaginosis is caused. It is an imbalance between the “good” bacteria and the “bad” bacteria inside the vagina. It seems to be more likely when sexual partners are changed and there is a high number of partners or indeed when vaginal washes are frequently used. It can be transmitted during sexual intercourse between women. Male partners of women who have Bacterial Vaginosis do not need any treatment.
Preventing Bacterial Vaginosis
Because the cause of Bacterial Vaginosis is not really known then the prevention is equally unknown. It is recommended to limit the number of sexual partners and not to use unnecessary vaginal washes . A good rule is to have periodic gynecologist examinations which can prevent this infection.
Bacterial Vaginosis symptoms
Many women show no symptoms even though they have Bacterial Vaginosis. Others experience vaginal discharge and unpleasant smells from the vagina, pain, itching or burning.
Inflammation of the Rectum and Colon
Inflammation of the anus, rectum or colon must be seen by a doctor for a correct diagnosis. They could be caused by sexually transmitted diseases (STD).
The inflammation of the rectum (proctitis) can cause pain to the anus and the inside of the rectum, difficultly in full bowel evacuation (tenesmus) with discharge from the anus. These symptoms must not be ignored and you must see a doctor for a correct diagnosis. During the medical visit you must inform the doctor of any unprotected anal sex you may have had.
The inflammation of the intestine (Enteritis) can have several causes with diarrhea and abdominal pain the most common symptoms. It is an infection transmitted by ingesting bacteria or parasites which are found in faeces and consequently in the genital and anal areas. These symptoms could be due to certain STDs so they must not be ignored particularly in HIV positive people. You must see a doctor for a correct diagnosis. During the medical visit you must inform the doctor of any unprotected anal sex you may have had.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease is an infection of the female genital organs mostly transmitted by sexual contact.
There can be no symptoms or there can be pain in the lower abdomen, fever , smelly discharge from the vagina, painful penetration during intercourse, burning sensation while urinating, blood loss during periods out with the menstrual cycle.
These symptoms can be those of certain STDs so they must not be ignored. A medical check-up is necessary for a correct diagnosis.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease can be prevented by using a condom during sexual intercourse.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Pregnancy
A pregnant woman can contract STDs the same as a non-pregnant woman. The pregnancy offers no protection to neither the mother nor the baby against STDs. Given that many STDs show no symptoms the pregnant woman must have herself check-out for all STDs including HIV. Their partners should take the same tests and if necessary follow any treatments scrupulously
An STD can complicate a pregnancy and provoke serious health issues for the mother and child. The child can have problems at birth or even years afterwards. Many of these problems can be cured with adequate health care during the pregnancy.
The risk of contracting diseases during pregnancy can be reduced by using a condom during all sexual intercourse.
The Prophylactic, the safe contraceptive
The prophylactic or condom is the safest contraceptive. It must be used from the beginning of the sexual activity, pulled over the erect penis before penetration
It should also be used during oral sex since it reduces the risk of contracting STDs.
Condoms are sexual precautions and must be kept in a dry plates and must not be exposed to direct sunlight. The wallet is not an ideal place to keep them and for those just passed their driving test, neither is the dashboard in your car. A small condom carrier is an ideal solution.
Always check the condom is in good condition. Even after being careful it could break during sex which you will realise only afterwards.
What should you do in this case? In the first place keep calm and don’t panic. You should go to your doctor and explain what happened, evaluate the probability of a pregnancy and take the relevant tests. If you are afraid of infection, don’t be afraid to talk about it and you will get the correct and relevant testing required.
This applies both to men and women!
